Mechanism of Action
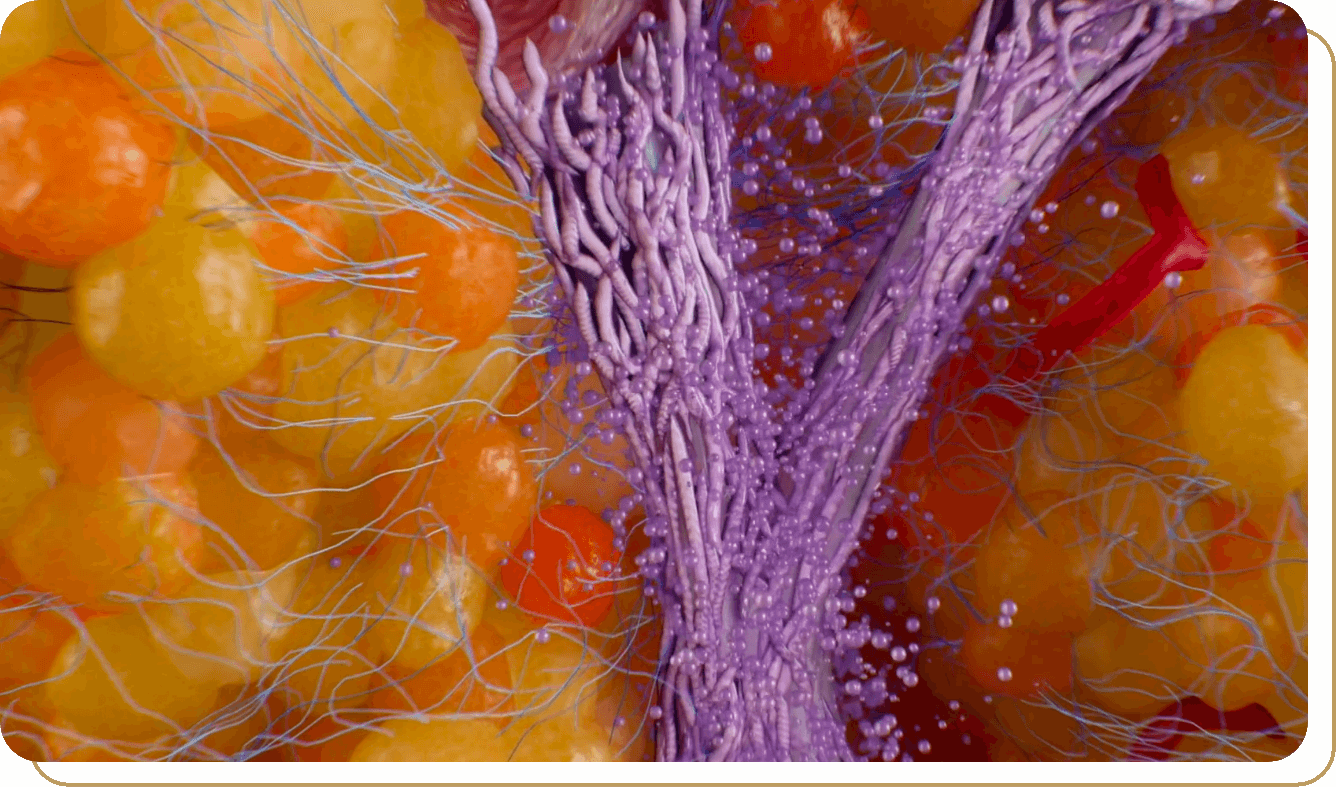
Three factors are involved in the development of cellulite:
 1
2
3
1
2
3
-
These collagen-rich bands tether the dermis to the underlying fascia and segment the fat layer into lobules.5,6
-
The fat lobules push up against the dermis; however, due to the septae tethering, they form mattress-like protrusions on the surface of the skin.5-7
-
Dermal thinning occurs, providing less support to contain the underlying soft tissues.5
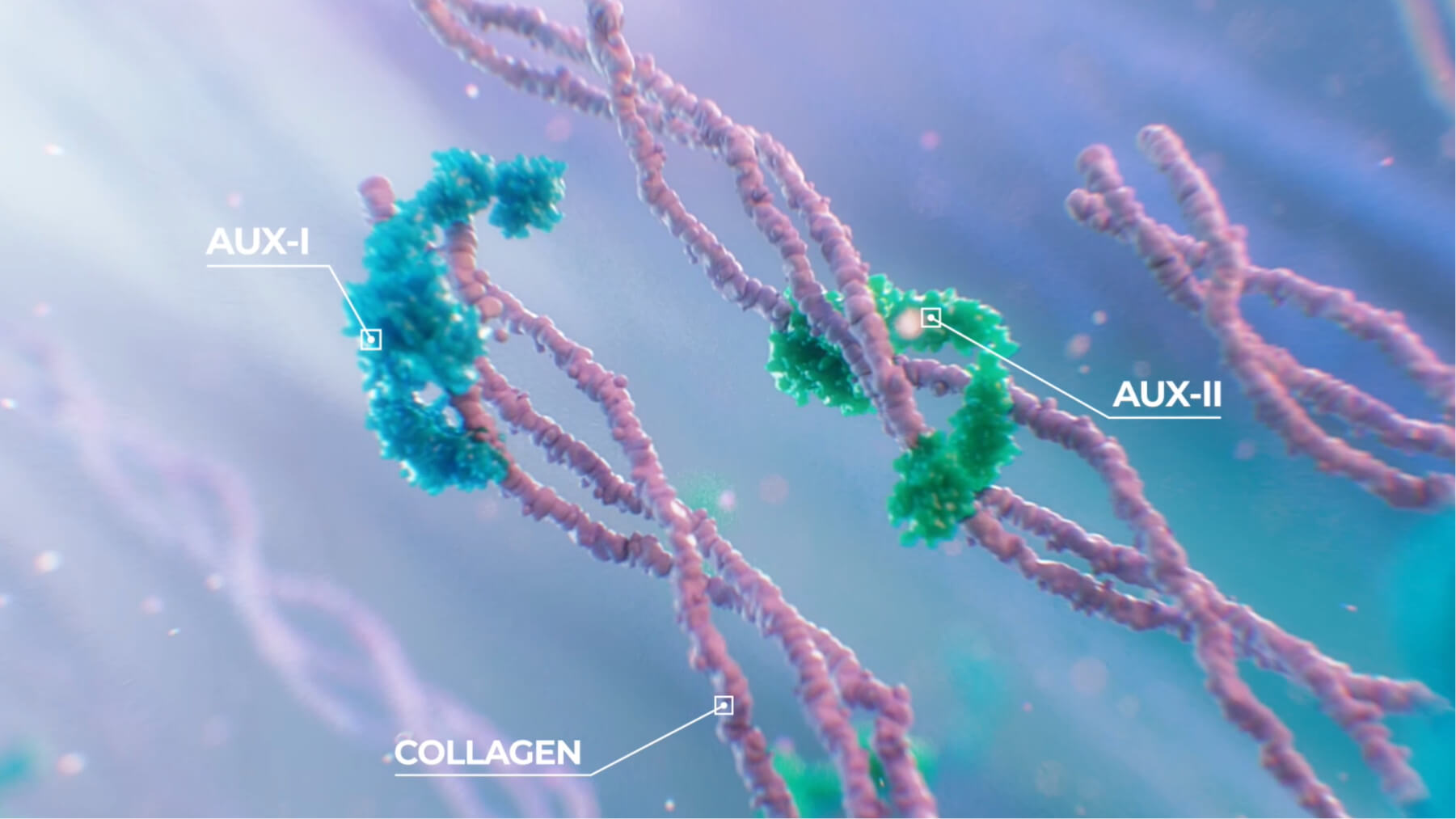
The exact mechanism for the treatment of moderate to severe cellulite is unknown.3 It is believed that QWO initiates a process called Enzymatic Subcision and Remodeling (ESR®), which includes three steps:8
Step 1
Enzymatic subcision
QWO is believed to treat cellulite by enzymatically subcising fibrous septae.3,8
Step 2
Fat lobule reorganization
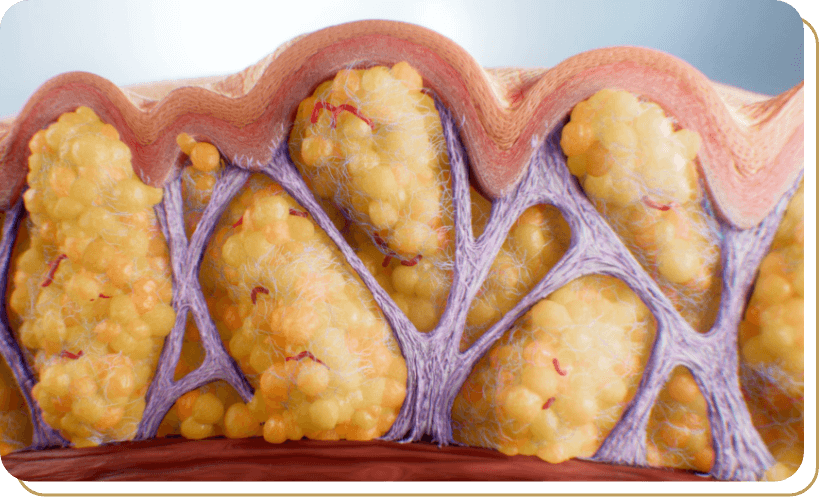
After subcision of fibrous septae, the fat lobules begin to reorganize and spread more evenly.8
The tension at the subdermal junction is released, allowing for fat lobules to be reorganized.4
Step 3
Collagen creation & dermal thickening
The enzymatic breakdown of the collagenous fibrous septae stimulates a wound healing-like reaction that results in the creation of new collagen, which helps thicken the dermis and rebuilds the collagen network.8,9
Over time, the fibrous septae may reform with new collagen, but will be thinner and smaller.8
ESR is believed to minimize cellulite dimples, giving the appearance of smoother skin.8
Mechanism of Action
Want to learn more about QWO?
Head over to the Clinical Education Center for more information.
Mechanism of Action Video